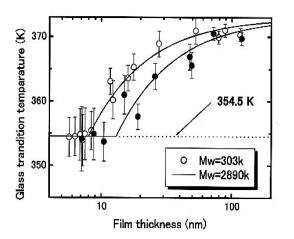
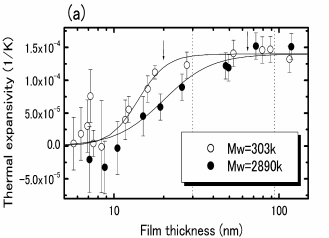
In order to study the origins of the decreases in glass transition temperature
and thermal expansivity with film thickness we performed inelastic neutron
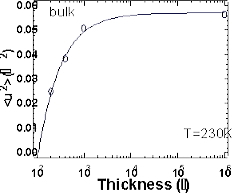
scattering, and found that mean square displacement <u2> and the
density of phonon states G(w) decrease with film thickness. These
decreases shjow the potential hardening in thin films, and have been assigned
to a hard layer at the interface between the polymer and substrate.
|
 |
 |
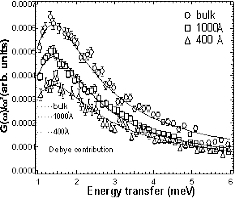 |
|
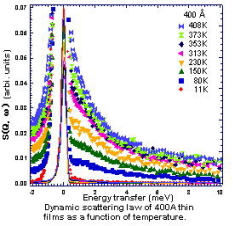
Dynamic scattering law
S(Q,w) of polymer thin film.
|
|
|
|
 |
Phys. Rev. Lett., 95. 56102 (2005))
Phys. Rev. E74, 021801 (2006)
|
| Cause of Potential Hardening is an interface hard layer beteeen polymer and substrate.
|
|
|
Phase Separation and Dewetting of Polymer Blend Thin Films
|
|
Phase separation and dewetting of polystyrene (PS) and Poly(vinyl methyl ether ) (PVME) blend thin films were studied as a function of film thickness by means of light scattering (LS), AFM, optical microscope, and neutron reflectivity.
|
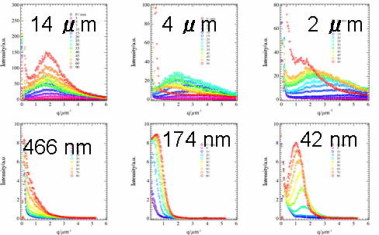 |
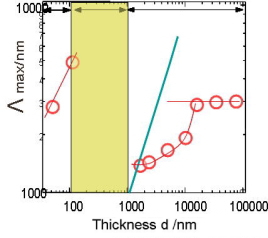 |
Time evolution of LS profiles
for various film thickness.
|
Film thickness dependence
of characteristic wavelength
|
In a range of thickness above 1ƒÊm, phase separation occurs preferentially,
and below 100 nm dewetting occurs preferentially. In between (100
nm - 1ƒÊm) phase separation and dewetting coexist and no characteristic
length is observed in LS profiles.
|
|
|
Concentration Fluctuations before Dewetting Revealed
by Neutron Reflectivity
|
|
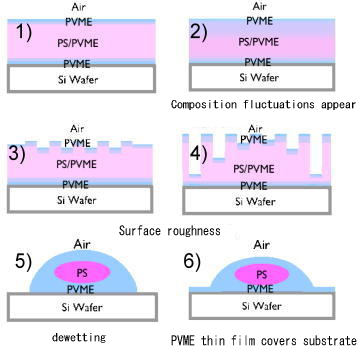
Dewetting process of PS/PVME blend thin film looks like spinodal decomposition
type one, however very long incubation time was observed. We have
studied the concentration fluctuations in thin films before dewetting by
neutron reflectivity, and found that they did. Another interesting
finding is a very thin layer formation of PVME after dewetting. This
must be due to the very high afinity of PVME to substrate.
|
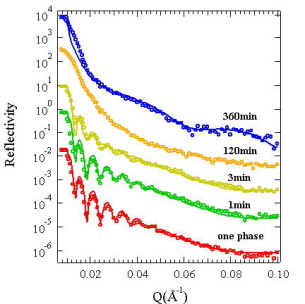 |
 |
Time evolution of NR profiles as a function
of annealing time.
|
|
|
|