(2)Slow Dynamics of Soft Matter
|
Dynamics near Glass Transition |
|
|
|
It is considered that glass transition is dynamic transition and extensive
studies have been performed, but it is still a mysterious problem in condensed
matter physics. Our group is studying dynamics glass-forming polymers
near Tg using quasielastic neutron scattering and dynamic light scattering.
|
|
◆Low energy excitation (Boson peak) and picosecond fast process in meV
region.
|
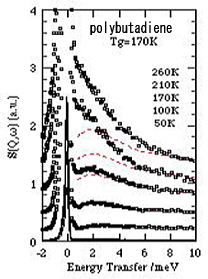
In most glass-forming materials the so-called boson peak is observed at
2-3meV far below Tg. The inelastic scattering intensity can be Bose-scaled.
On the other hand, the picosecond fast process appears at around Tg as
an excess quasielastic scattering intensity. The origins of
the Boson peak and the fast process are still under discussion.
|
|
J. Chem. Phys., 95, 5332 (1991)
J. Chem. Phys., 98, 8262(1993)
J. Chem. Phys., 104, 3841-3850 (1996)
J. Chem. Phys., 108, 6492-6497 (1998)
|
Temperature dependence of S(Q,w) of polybutadiene. Red dashed lines
are the expected intensities from the Bose factor.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
◆E-process appearing in glass-forming polymers near Tg
|
We found that E-process appears in glass-forming polymers near Tg in sub-nanosecond
region. This E-process corresponds to elementary process for conformation
transition in polymer, which is predicted by MD simulations.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
Macromolecules, 24, 1826 (1991)
Macromolecules, 32, 1672 (1999)
|
|
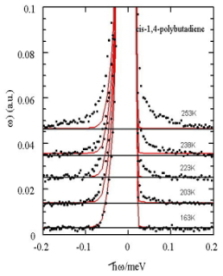
Temperature dependence of S(Q,w) of polybutadiene in sub-nanosecond region
(several tens ?eV)
|
|
◆α-process (segemental motion)
|
Glass transition is directly governed by the ?-pprocess. We performed dynamic
light scattering (photon correlation spectroscopy) measurements on the
?-process of a glass forming polymer PMpTS. The correlation function can
be well described by a stretched exponential function, showing a wide distribution
of relaxation time in the a-process. This is an origin of dynamic
heterogeneity in glass-forming-materials.
|
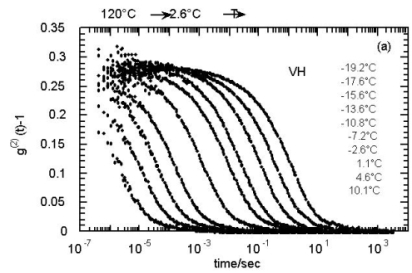 |
Intensity correlation function of the a-process in PMpTS observed by dynamic
light scattering.
|
|
|
|
|
◆Local dynamics of a glass-forming polymer studied by thermal neutron spin-echo
technique
|
|
Thermal neutron spin echo machine:
TASSE in Tokai

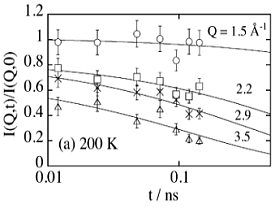
Intermediate scattering function I(Q,t) of polybuadiene
|
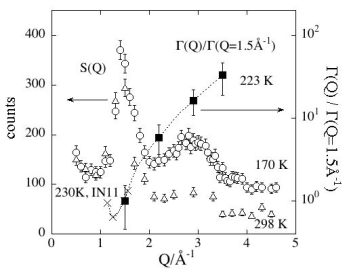 |
Q-dependence of structure factor S(Q) and decay rate ? of polybutadiene.
de Gennes narrowing is observed at Q=1.5A-1, but not at Q=2.9A-1.
? increases with Q monotonously.
|
|
J. Phys. Soc. Japan, 74, 3236 (2005)
|
|
|
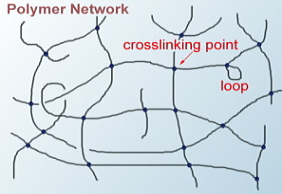
Dynamics of Polymer Gels
Static and Dynamic Fluctuations
|
|
It is essential to elucidate dynamics of polymer gels to understand the
response to external stimulations. We have studied the gel dynamics
using neutron spin-echo (NSE) technique, which is one of the rare
methods proving nm scale dynamics directly. In the series of
the studies we have investigated three types of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)
gels (I) PVA gels formed in mixed solvent of DMSO and water, (ii) PVA gels
formed in borax aqueous solutions (iii) chemically cross-linked PVA gels
by GA, to separate fluctuations into static and dynamic fluctuations.
|
|
|
 |
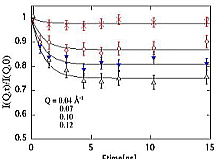
Neutron spin-echo measurements
Non-decaying component (static fluctuations) and decaying component (dynamic
fluctuations), which cannot be separated by small-angle neutron scattering,
have been separated by NSE measurements.
|
 |
|
◆Corss-linking points and NSE data |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
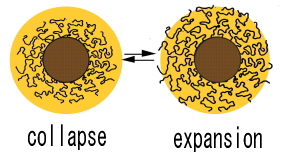
Static fluctuations are dominant:
hard gel
|
|
Fluctuations are all dynamic:
Soft gel
|
|
Static fluctuations increase with density of cross-links
|
|
|
|
J. Neutron Res., 10, 149 (2002)
Phys. Rev. E71, 011801 (2005)
Physica B, in press (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
Dynamics of polymer micelles
|
|
Breathing mode in grafted polymer chains on a flat surface in a good solvent
has been predicted by de Gennes. This mode is driven by competition
between the osmotic pressure and entropic force of polymer chains.
We have performed neutron spin echo (NSE) measurements on polymer chains
in corona part of polymer micelles to elucidate the breathing mode.
The breathing mode was proved in polyisoprene/polystyrene (PI-PS) diblock
copolymer, but not in polybutadine/polystyrene (PB-PS). This has
been attributed to difference of the second virial coefficient.
|
|
|
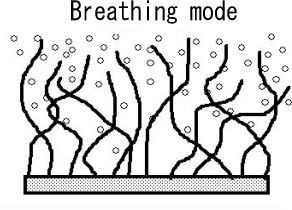
Breathing mode in polymer micelles
 |
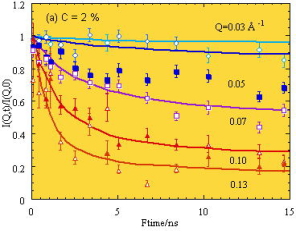
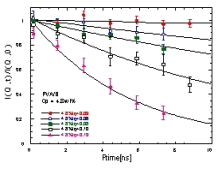
Intermediate scattering function I(Q,t) of PI-PS diblock copolymer and
theoretical curves for breathing mode.
|
J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 60, 1367-1369 (1999)
|
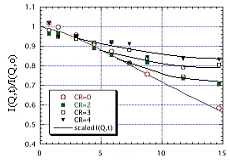
Breathing mode disappears in PB-PS diblock copolymer micelle. This
is due to small second virial coefficient of PB chains.
|
| J. Chem. Phys., 122, 144905 (2005) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dynamics of aqueous polyelectrolyte solutions
|
|
In polyelectrolyte solutions the structure is dominated by long range electrostatic
interactions. Dynamics is also affected by the interaction and de
Gennes narrowing is observed at the peak position of structure factor S(Q).
On the other hand, detailed studies by neutron spin echo elucidated that
degree of internal freedom also affects the dynamics very much.
|
Q-dependence of Dapp & S(Q)
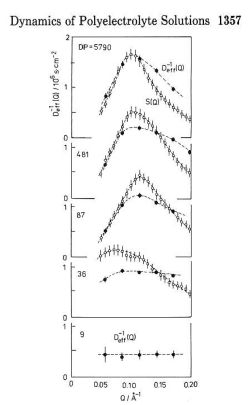
|
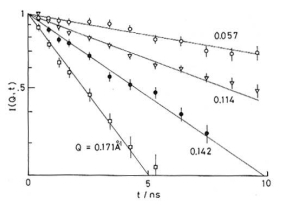
|
| Macromolecules, 22, 1356 (1989)
|
|
|
|
|




















